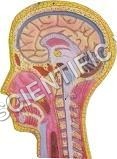
HUMAN HEAD AND NECK
Product Details:
- Material PVC
- Usage Nursing Institutes & Medical college, Hospitals
- Color Skin
- Product Type Human Head
- Type Medical Model
HUMAN HEAD AND NECK Price And Quantity
- 1 Piece
- 107 INR/Piece
HUMAN HEAD AND NECK Product Specifications
- Medical Model
- PVC
- Nursing Institutes & Medical college, Hospitals
- Human Head
- Skin
HUMAN HEAD AND NECK Trade Information
- Cash in Advance (CID) Cash Advance (CA)
- 100 Piece Per Week
- 1 Week
- Yes
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Western Europe Australia Eastern Europe Middle East Central America South America Asia North America Africa
- All India
Product Description
HUMAN HEAD AND NECK:-
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is diagnosed in approximately 500,000 individuals worldwide each year [1]. Major risk factors are smoking, smokeless tobacco, betel nut chewing, and alcohol consumption.
However, many patients with oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas, particularly those arising in the base of the tongue and in the tonsillar region, do not have any of these risk factors. Epidemiologic and molecular studies have identified the HPV-16 type of human papillomavirus (HPV) as a causative agent in these patients [2,3]. Other HPV types such as HPV-18, 31 or 33 are much less common. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the most commonly diagnosed sexually transmitted disease in the United States. In addition to oropharyngeal cancer, HPV-16 is associated with condyloma acuminatum, squamous intraepithelial lesions and anogenital malignancy including cervical, vaginal, vulval, penile, and anal carcinoma.